
The EU Member States (High school)
Objective: This worksheet aims to teach students about the origin, development, and current situation of the European Union, including its member states and accession candidates, and to encourage critical thinking about its opportunities and challenges for the future.
Content and methods: The worksheet provides a comprehensive text on the history and evolution of the EU, from its early foundations to modern developments and key events like Brexit. It includes a timeline for students to fill in, requiring them to extract information about significant milestones and accessions. Additionally, it features a table of current EU member states and their entry dates. A detailed profile of a EU candidate country is presented, which students then use to complete a profile sheet and answer questions, thereby engaging with both factual recall and analytical thinking. The tasks also prompt students to describe the EU's development in their own words and discuss its future opportunities and challenges.
Competencies:
- Reading comprehension
- Chronological understanding and timeline completion
- Information extraction and summarization
- Analysis of political and economic information
- Critical thinking about international cooperation and challenges
- Understanding of geographical and demographic data
Target group: 8th-10th grade
54 other teachers use this template
Target group and level
Grade 8 and above
Subjects
The EU Member States (High school)

The European Union
Read the text about origin and development of the EU and fill in the timeline on the following page.
Origin and development of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a political and economic union of currently 27 European states, whose origins date back to the post-World War II era. The idea of a united Europe arose from the desire to promote lasting peace and economic stability. The first step in this direction was taken in 1951 with the founding of the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) by the six founding states Belgium, Germany, France, Italy, Luxembourg, and the Netherlands.
In 1957, the European Economic Community (EEC) and the European Atomic Energy Community (EURATOM) were established by the Treaties of Rome. These treaties formed the basis for economic integration and the creation of a common market. The EEC developed further in the following decades and continuously increased its number of members.
A significant milestone was the accession of the United Kingdom, Ireland, and Denmark in 1973. This was the first enlargement of the community and marked the beginning of a phase of continuous expansion. In the 1980s, Greece (1981), Portugal, and Spain (both 1986) joined the community.
The collapse of communism in Eastern Europe at the end of the 1980s and the beginning of the 1990s led to another wave of enlargement. In 1995, Austria, Finland, and Sweden joined the EU. The largest enlargement took place in 2004 when ten countries, including many former Eastern Bloc states like Poland, Hungary, and the Czech Republic, joined the EU. Bulgaria and Romania followed in 2007, and Croatia became the 28th member in 2013.
Parallel to its enlargement, the EU deepened its integration. The Maastricht Treaty, signed in 1992 and entering into force in 1993, created the European Union in its current form and introduced a common currency, the Euro, which was launched in 1999. Other important treaties such as the Amsterdam Treaty (1997), the Nice Treaty (2001), and the Lisbon Treaty (2007) reformed the EU's institutional structures and expanded its competences.
A significant event in the history of the EU was the exit of the United Kingdom, known as Brexit. Following a referendum in 2016, in which a narrow majority of Britons voted to leave, the United Kingdom officially left the EU on January 31, 2020. This was the first time a member state left the union and posed new challenges for both the EU and the United Kingdom.
The EU remains a unique project of international cooperation, promoting peace, stability, and prosperity in Europe while simultaneously facing diverse political and economic challenges.
Current EU member states
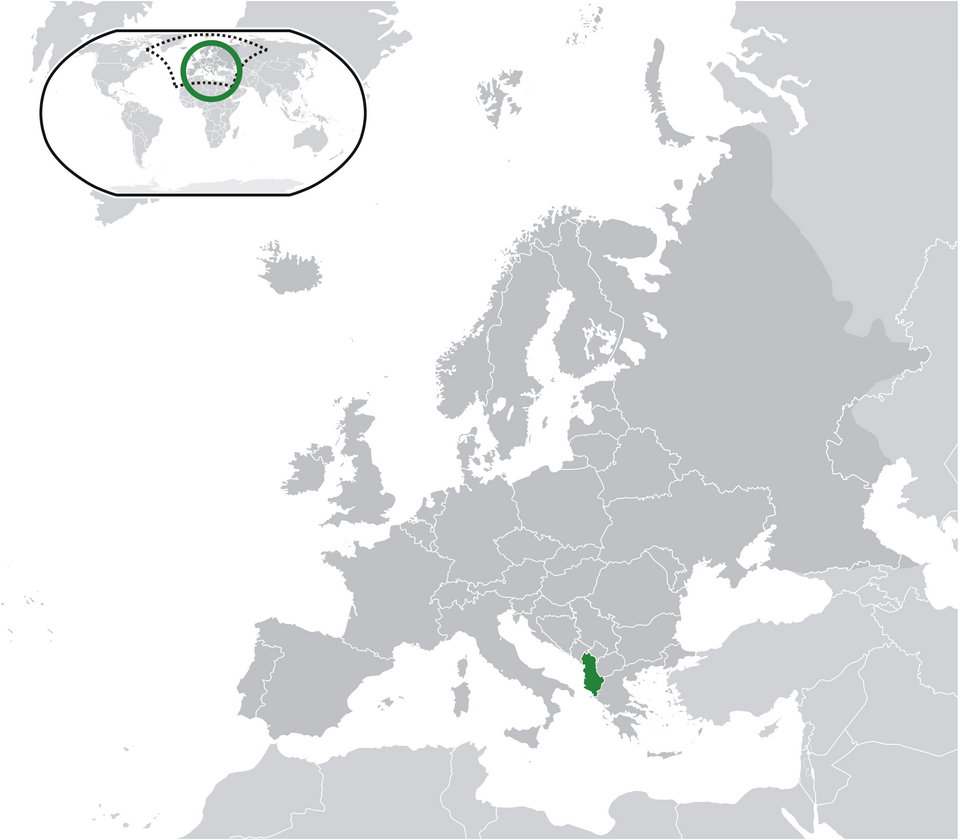
Albania
Source: Wikipedia
Albania, officially the Republic of Albania, is a small country in Southeast Europe on the Balkan Peninsula. It borders Montenegro to the northwest, Kosovo to the northeast, North Macedonia to the east, and Greece to the south, with coastlines on the Adriatic Sea to the west and the Ionian Sea to the southwest. With a total area of 28,748 square kilometers, Albania is characterized by a diverse geography that includes mountains, plains, and a beautiful coastline. The country has a population of approximately 2.4 million people, with Tirana as its vibrant capital and largest city.
Albania's political landscape is marked by its transition from a communist state to a parliamentary republic. Currently, it is governed by a unitary parliamentary republic system, with Bajram Begaj serving as the President and Edi Rama as the Prime Minister. The political situation remains dynamic, with efforts focused on democratic reforms and combating corruption to align with European Union standards.
Economically, Albania has made significant strides since the collapse of communism, shifting from a centrally planned economy to an open-market system. The country's economy is diverse, with key sectors including agriculture, manufacturing, and services. However, challenges such as high unemployment rates and emigration persist. Despite these hurdles, Albania's economy has shown resilience, with gradual improvements in infrastructure and foreign investment.
Albania's EU accession journey has been a central focus of its political agenda. The country applied for EU membership in 2009 and was granted candidate status in 2014. While progress has been made in various sectors, Albania continues to work on meeting the EU's stringent criteria, particularly in areas such as the rule of law, judicial reform, and anti-corruption measures. The Albanian government and its citizens generally view EU membership as a strategic goal that promises economic benefits, political stability, and enhanced international standing.
One of Albania's unique features is its rich cultural heritage, influenced by various civilizations, including the ancient Greeks, Romans, Byzantines, and Ottomans. The country boasts several UNESCO World Heritage Sites, such as the ancient city of Butrint and the historic centers of Berat and Gjirokastër. Albania's natural beauty, with its pristine beaches, rugged mountains, and picturesque landscapes, makes it an emerging destination for tourism.
In conclusion, Albania's journey towards EU membership reflects its aspirations for a stable and prosperous future. Despite the challenges, the country's commitment to reforms and its rich cultural heritage position Albania as a unique and promising candidate for the European Union.

Additional information for teachers
