
Philosophers of the World
Objective: The overarching learning objective of this worksheet is to broaden students' understanding of philosophical thinkers from diverse cultures and to encourage critical engagement with their ideas and their relevance to contemporary issues.
Content and Methods: This worksheet introduces students to different philosophy, detailing its historical context, central themes such as the harmony of reason and faith, and key figures. It outlines their individual contributions and major works. The methods employed include reading informative texts, answering multiple-choice questions to assess comprehension, and engaging in analytical writing tasks such as explaining philosophical concepts, summarizing individual contributions, and applying historical philosophical ideas to current global problems, with a requirement to justify their potential helpfulness.
Competencies:
- Reading comprehension (understanding complex philosophical texts).
- Critical thinking (analyzing philosophical concepts and their relevance).
- Information synthesis (summarizing key ideas and contributions).
- Argumentation and evaluation (applying historical ideas to current problems and justifying their helpfulness).
- Cross-cultural understanding (exposure to non-Western philosophical traditions).
- Written expression (formulating clear and concise explanations and arguments).
Target Audience and Level:
Grade 8 and above
53 other teachers use this template
Target group and level
Grade 8 and above
Subjects
Philosophers of the World

When you think of famous philosophers, which names come to your mind?
Collect your results in class. What do you notice?
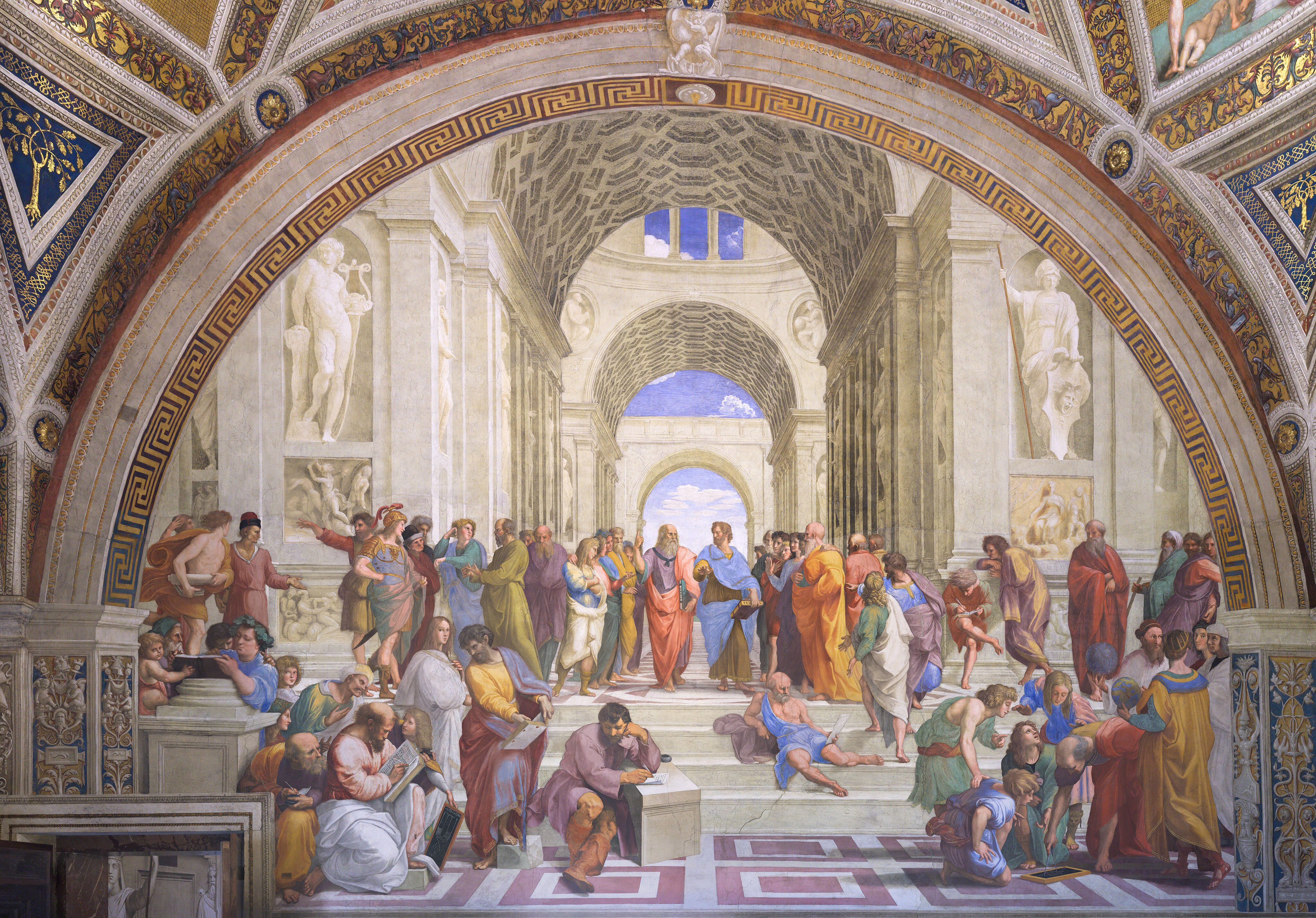

Raphael: "The School of Athens"
Philosophers of the World
As you have probably noticed, most of the philosophers we encounter in school and daily life are male and belong to our Western cultural tradition. But that is only a small part of the philosophical world! There are many other philosophers from different cultures who have developed exciting and important ideas. That’s why this worksheet focuses on thinkers who are often less well-known but whose perspectives are just as fascinating and meaningful.
The World of Islamic Philosophers
Islamic philosophy is a fascinating and rich tradition that emerged from the Islamic world, blending religious beliefs with logical reasoning, mathematics, and sciences. This blend, often referred to as "falsafa" (philosophy) and "kalam" (theology), sought to understand the universe, existence, and the nature of God.
The journey of Islamic philosophy began during the Golden Age of Islam, roughly from the 8th to the 12th centuries. This era saw the rise of great thinkers like Al-Kindi, who is often considered the first Islamic philosopher, and Al-Farabi, who was known for his works on political philosophy and metaphysics. This period also saw the works of Avicenna (Ibn Sina) and Averroes (Ibn Rushd). These philosophers were heavily influenced by Greek philosophy, particularly Aristotle and Plato, and they sought to harmonize this with Islamic teachings.
Islamic philosophy dealt with several central themes, including the nature of God, the creation of the universe, the soul, and ethics. Philosophers explored questions about free will and predestination, the existence of an afterlife, and the nature of knowledge and truth. They also made significant contributions to science, medicine, and mathematics, influencing the intellectual landscape of both the Islamic world and medieval Europe.
Despite facing opposition from some religious scholars who believed that philosophy could lead to heresy, Islamic philosophers managed to leave a lasting legacy. Their works were translated into Latin and Hebrew, impacting European thought and playing a crucial role in the Renaissance.
Islamic philosophers were not just confined to religious and metaphysical questions; they also engaged deeply with practical issues, including politics, ethics, and education. Their intellectual pursuits laid the groundwork for many modern scientific and philosophical ideas, demonstrating the timeless quest for knowledge and understanding.
Al-Farabi

Avicenna

Averroes
